Reflection站在东门可以望穿西门的贸大 NXWYR03 刷屏第八弹,为四位数而奋斗!你可以骂我但请不要打我。 | ||
大一下,根据文章Institutions, resources, and entry strategies in emerging economies 和Survey of leadership styles in different cultures写的reflection,语言依旧中式,觉得比较可取的是将两篇文章联系起来做的简单模型建立和思考假设。 小荷作文网 www.zww.cn Introduction Problem Statement Leadership is the process of having dominance on group activities so as to realize the objectives; it could also be defined as influencing teamwork with the aim of securing certain goals. However, faced with different countries and various cultures, leadership also contains different styles. According to the leadership –culture sdudies, there are two types of leadership: task oriented and people oriented. Then the authers analyse the leadership styles in some selected countries and the models of it, they also discuss about cross-cultural leadership concept and its challenges. Objectives of the Paper The paper studies the relation between cultures and styles of leadership in different countries in order to get a comparative analysis made over by various leadership styles, and it helps to choose a proper style of leadership for each situation. Methodology The research into the leadership-culture stuies Establish a model by combing the direction-goal model of Robert House and dividing cultural dimensions done by Geert Hosfstede. Do the survey in order to investigate the leadership fashion in multiple countries and have a comparative analysis. Analyse the studies and the models made by other experts, such as Dikson’s cross-cultural leadership and so on. Discuss and couclude all the factors of the leadership, especially the cultural factor. 1. Diversity in Leadership style 1.1Intercultural leadership contingency model According to the paper, this model is classified into 4 categories: directional lead-ership, supportive leadership, participatory leadership and success oriented lead-ership. Different country or company chooses a different but suitable leadership style. 1.2 Balance of the 4 categories Each style has its advantages and disadvantages and it’s impossible to define which is best, because if it exist, it must be possible. Every country has its own culture and situation, and the company should analyse its environment and com-bine 4 styles (by deciding a proportion of each style) to build a balanced model of leadership. However, the main body of the style should be maintained. 2. R/I/LS-Model (Resources/Institutions/Leadership Style-Model) 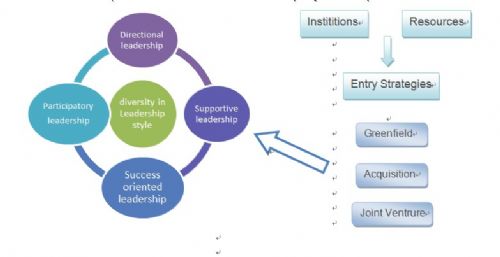 Fig.: R/I/Ls Model 2.1 Introduction of the R/I/LS model This leadership style model is considered about those foreign direct investment (FDI)companies. The modes of establishing an FDI project can be classified into three types: Greenfield, acquisition, and joint venture. Taking institutions and re-cources into consideration, we can choose a proper style for those companies. 2.2 Directional Leadership Directional leadership prepares guides for staff about what they should do and how to perform it, work planning, and functional standards. The superiors can direct and instruct the inferiors so as to lead them to work in their maximum capacity and ability. Hypotheses 1: It is suitable for joint FDI companies because it can be effective-ly controlled by the superiors. 2.3 Supportive Leadership Supportive leadership pays attention to welfare of the staff and their requirements, and establishes friendly relationships with staff and conducts equal behaviors toward all staff. In this case, inferiors and the superiors are available to communicate. Hypotheses 2: If institutions are strong and there is need tangible resources, it is beneficial to all those FDI companies because such a friendly atmosphere can avoid the conflits between various different cultures. 2.4 Participatory Leadership Participatory leadership consults with staff and pays serious attention to their attitudes during decision making. It stresses the significance of teamwork and it is widely used all over the world. Hypotheses 3: When it is placed in the FDI companies, our hypothesis is that it can work but it may not work as good as the other styles, it is needed in some way but the percentage of this kind of model in the leadership can not be so large. 2.5 Success Oriented Leadership Success oriented leadership encourages staff to perform works to the highest levels, determines the goals to such an extent that they can be realized with challenges, expresses trust in high abilities of the staff, which means an aggressive goal for both of them. In this case, it may be the best choice for WOE. While in many emerging economies, weak institutional arrangements may mag-nify information asymmetries so firms face higher partner-related risks and need to spend more resources searching for information. It may cause some conflicts in a weak institutional framework. So in an environment of strong institutional frame-work and tangible resources, perhaps they would also achieve its highest goal. Hypotheses 4: If institutions are weak and there is need tangible resources, then a success-orient LS should be necessary. |